Understanding CMC Injury: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
CMC injury is a significant concern for many individuals, especially those involved in activities that require repetitive hand or thumb movements. This type of injury can lead to pain, discomfort, and reduced functionality of the hand. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for CMC injury is vital for anyone looking to maintain their hand health and prevent long-term complications.
Identifying the early signs of a CMC injury can be crucial for effective treatment. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of CMC injury, including its causes, symptoms, and the various treatment options available. Whether you are an athlete, a manual laborer, or someone who engages in hobbyist activities that require fine motor skills, this information can help you better understand how to protect your hands.
By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of CMC injury and be equipped with the knowledge to seek appropriate medical attention if necessary. Let’s dive into the details of this common yet often misunderstood injury.
Table of Contents
- What is CMC Injury?
- Causes of CMC Injury
- Symptoms of CMC Injury
- Diagnosis of CMC Injury
- Treatment Options for CMC Injury
- Prevention of CMC Injury
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion
What is CMC Injury?
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is located at the base of the thumb, where the thumb connects to the wrist. CMC injury refers to damage or stress to this joint, which can occur due to various factors, including repetitive strain, trauma, or degenerative conditions.
Common types of CMC injuries include:
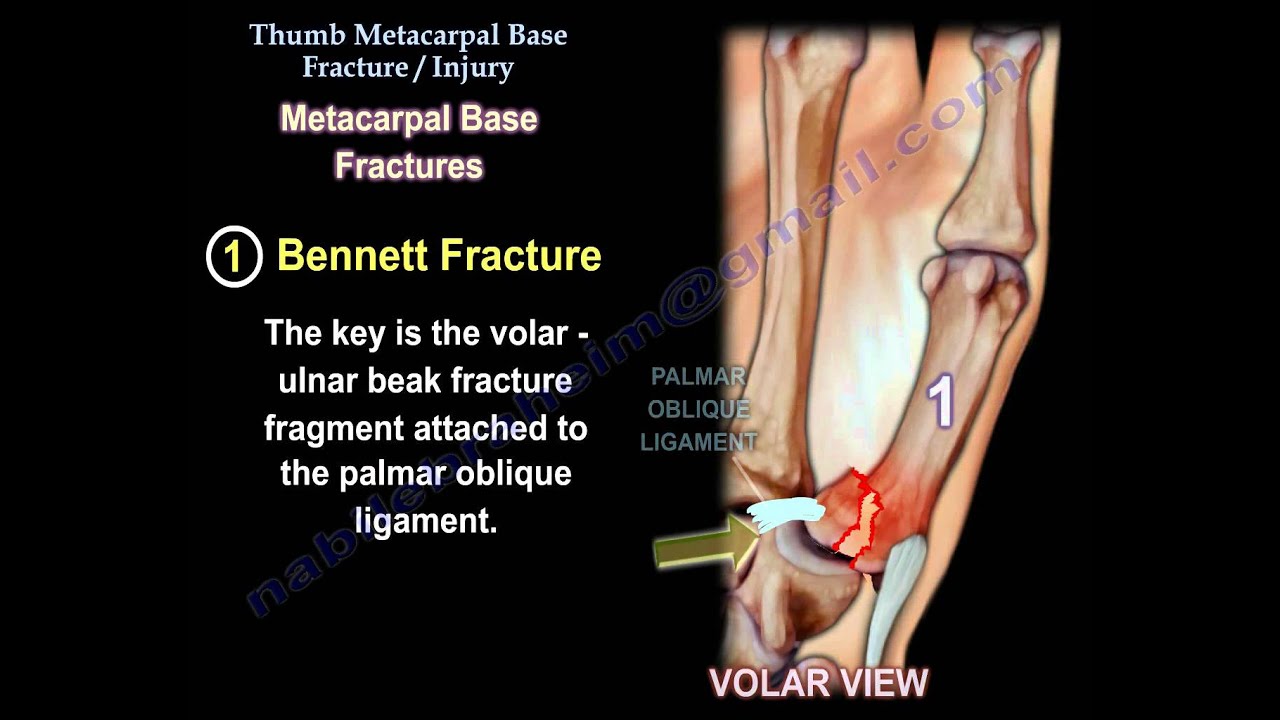
- Sprains: Overstretching or tearing of ligaments around the CMC joint.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones surrounding the CMC joint.
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage in the CMC joint, leading to pain and stiffness.
Causes of CMC Injury
Several factors can contribute to the development of a CMC injury, including:
- Repetitive Use: Activities that involve repetitive thumb motions, such as typing, playing musical instruments, or certain sports, can lead to overuse injuries.
- Acute Trauma: A sudden injury, such as a fall or direct impact to the hand, can cause CMC joint injuries.
- Aging: As we age, the cartilage and ligaments in our joints can weaken, increasing the risk of injuries.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to joint issues, making them more susceptible to CMC injuries.
Symptoms of CMC Injury
Identifying the symptoms of a CMC injury is crucial for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Pain at the base of the thumb, especially during movement.
- Swelling and tenderness around the CMC joint.
- Stiffness or decreased range of motion in the thumb.
- A popping or grinding sensation when moving the thumb.
Understanding the Severity of Symptoms
Symptoms can vary in severity depending on the type and extent of the injury. Mild injuries may cause temporary discomfort, while severe injuries can lead to chronic pain and significant functional impairment.
Diagnosis of CMC Injury
To accurately diagnose a CMC injury, healthcare professionals typically perform the following steps:
- Medical History: Discussing symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries.
- Physical Examination: Checking for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion in the thumb and wrist.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to assess bone and soft tissue damage.
Treatment Options for CMC Injury
Treatment for CMC injury will depend on the severity of the injury and may include:
- Rest: Taking a break from activities that exacerbate pain.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in exercises to improve strength and flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged structures.
Prevention of CMC Injury
Preventing CMC injuries involves a combination of proper technique and good habits:
- Ergonomics: Ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed to minimize strain on the hands.
- Stretching: Regularly stretch and strengthen hand and thumb muscles.
- Breaks: Take frequent breaks during repetitive tasks to prevent overuse.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or a decrease in thumb function, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent further complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
CMC injury is a common issue that can significantly impact daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their hand health. If you suspect you have a CMC injury, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Additionally, share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below, and feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on hand health.
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has provided valuable insights into CMC injury and encourages you to prioritize your health and wellness.
The Incredible Story Of The 1972 Andes Plane Crash Survivors
Understanding U Stock: A Comprehensive Guide To Your Financial Future
NOC: Understanding Network Operations Center And Its Importance